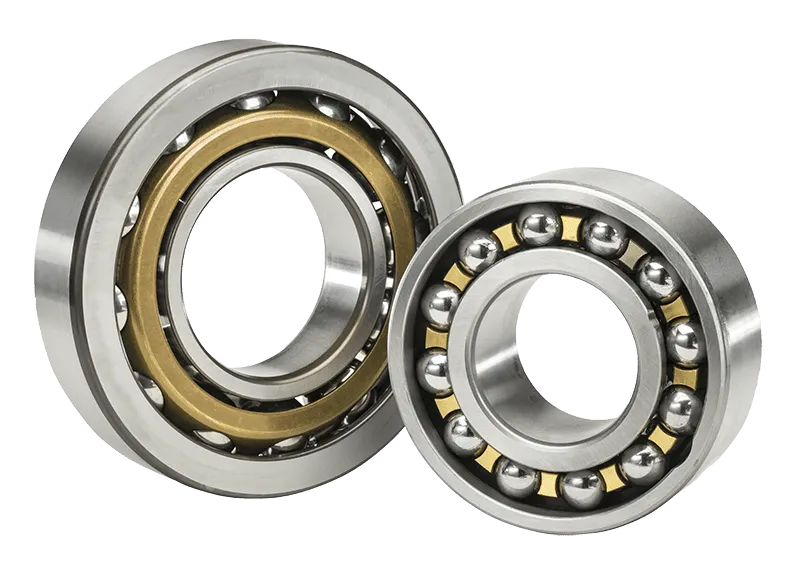

Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are precision-engineered components designed to reduce friction and support radial and axial loads by using balls as the rolling elements between the inner and outer rings.
- "Supports radial and axial loads up to 20% higher."
- "Precision tolerance of up to ±0.001 mm for smooth rotation."
- "Rated for speeds exceeding 10,000 RPM in optimal conditions."
Types
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: These bearings are the most common type and have a deep raceway groove, making them suitable for radial and axial loads in various applications, including motors, pumps, and household appliances.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: As previously described, angular contact ball bearings are designed to handle combined radial and axial loads by using angled contact points between the balls and raceways.
- Thrust Ball Bearings: These bearings are designed to accommodate axial loads in one direction and are commonly used in automotive applications, such as gearboxes and steering systems.
- Self-Aligning Ball Bearings: Self-aligning ball bearings have two rows of balls and a concave raceway in the outer ring, allowing them to compensate for shaft misalignment. They are used in applications where shaft deflection or misalignment is likely, such as agricultural equipment and textile machinery.
Features and Benefits

- Low Friction: Operates with low friction, ensuring efficient energy transfer and reduced heat.
- High Speed: Capable of high-speed operation, maintaining stable contact between balls and raceways.
- Versatility: Various designs meet different application needs, offering flexibility in loads and speeds.
- Quiet Operation: Minimal noise and vibration make them ideal for low-noise applications and precision equipment.
- Durability: Designed to withstand harsh conditions, providing long-lasting performance in demanding environments.
- Compact Design: Small size allows for easy integration into various systems, saving space and weight.
Applications

- Automotive: Ball bearings are widely used in automotive applications, including wheel hubs, transmissions, and steering systems, due to their ability to handle radial and axial loads efficiently.
- Industrial Machinery: They are essential components in industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and machine tools, where reliable performance and durability are critical.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, ball bearings are used in landing gear, control systems, and actuators, providing reliable performance under extreme conditions and stringent safety requirements.
- Consumer Electronics: From computer hard drives to household appliances, ball bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation in everyday consumer electronics.
Selection Considerations
- Load Capacity: Choose the appropriate type and size of ball bearing based on the expected radial and axial loads in the application.
- Speed Capability: Consider the operating speed range and the bearing's ability to maintain stable performance at high speeds without excessive heat generation or wear.
- Environmental Conditions: Evaluate factors such as temperature, moisture, and contaminants to select bearings with appropriate seals or coatings for extended service life and reliability.
- Installation and Maintenance: Follow manufacturer recommendations for installation procedures and maintenance intervals to ensure optimal performance and longevity of ball bearings in service.
