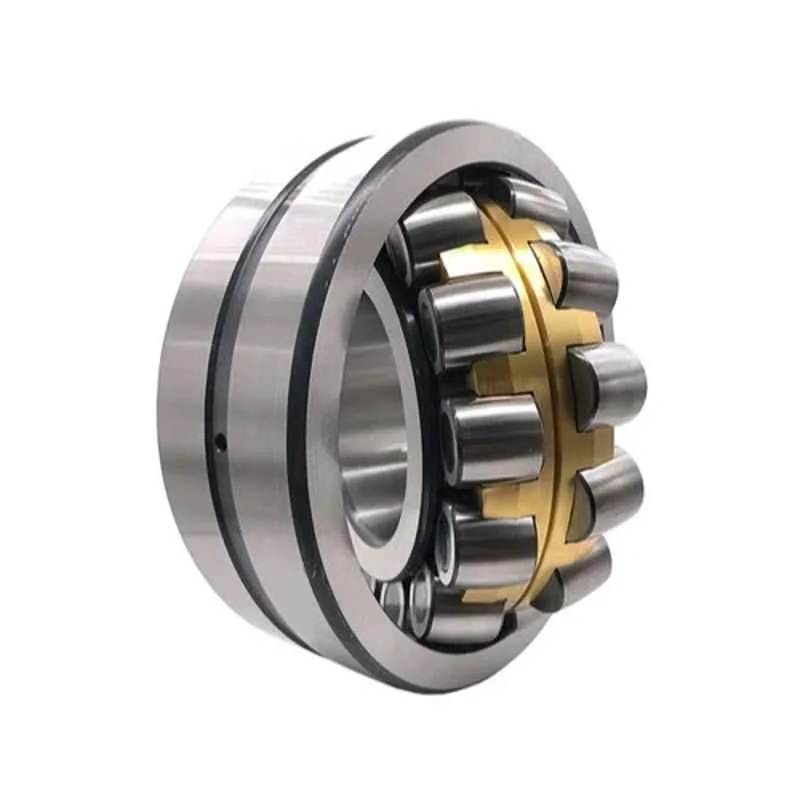

Spherical Bearings
Spherical bearings, also known as spherical plain bearings or spherical rod ends, are mechanical bearings that accommodate angular misalignment between two machine components. They typically consist of an inner ring with a spherical convex outside surface and an outer ring with a correspondingly concave inside surface.
- Misalignment Tolerance: Can accommodate angular misalignment of up to 7°.
- Load Capacity: Capable of handling heavy radial and axial loads, typically up to 200 kN.
- Operating Temperature Range: Functions effectively in a temperature range from -40°C to 200°C.
Types
- Radial Spherical Plain Bearings: These bearings are designed to support predominantly radial loads and accommodate angular misalignment. They are commonly used in applications where oscillating or reciprocating motion is present, such as hydraulic cylinders and steering linkage joints.
- Angular Contact Spherical Plain Bearings: Similar to radial spherical plain bearings but with the addition of angular contact capability, these bearings can also handle axial loads in addition to radial loads. They are suitable for applications requiring both radial and axial load support, such as heavy-duty construction equipment and mining machinery.
Features and Benefits

- Angular Misalignment: Accommodates misalignment, reducing stress and wear on connected parts.
- High Load Capacity: Supports heavy radial and axial loads for demanding applications.
- Maintenance-Free: Available in self-lubricating or sealed designs for reduced maintenance.
- Corrosion Resistance: Features materials or coatings to resist corrosion in harsh environments.
- Durability: Ensures long-lasting performance in challenging industrial and environmental conditions.
Applications

- Automotive: Spherical bearings are used in suspension systems, steering linkages, and ball joint applications in vehicles to handle dynamic loads and vibrations.
- Industrial Machinery: They find applications in industrial equipment such as hydraulic cylinders, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment where reliable performance under heavy loads and harsh conditions is essential.
- Aerospace: Spherical bearings are employed in aircraft landing gear, flight control systems, and engine mounts to withstand high loads and vibrations encountered during flight operations.
Selection Considerations
- Load Ratings: Select bearings with adequate load ratings to support the expected radial and axial loads, considering both static and dynamic load conditions in the application.
- Misalignment Capacity: Evaluate the degree of misalignment expected during operation and choose bearings with sufficient angular misalignment capability to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider factors such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to contaminants when selecting bearings, opting for designs with appropriate sealing or protective features for enhanced performance and reliability.
- Mounting and Installation: Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper mounting techniques and alignment procedures to maximize bearing performance and minimize premature wear or damage.
