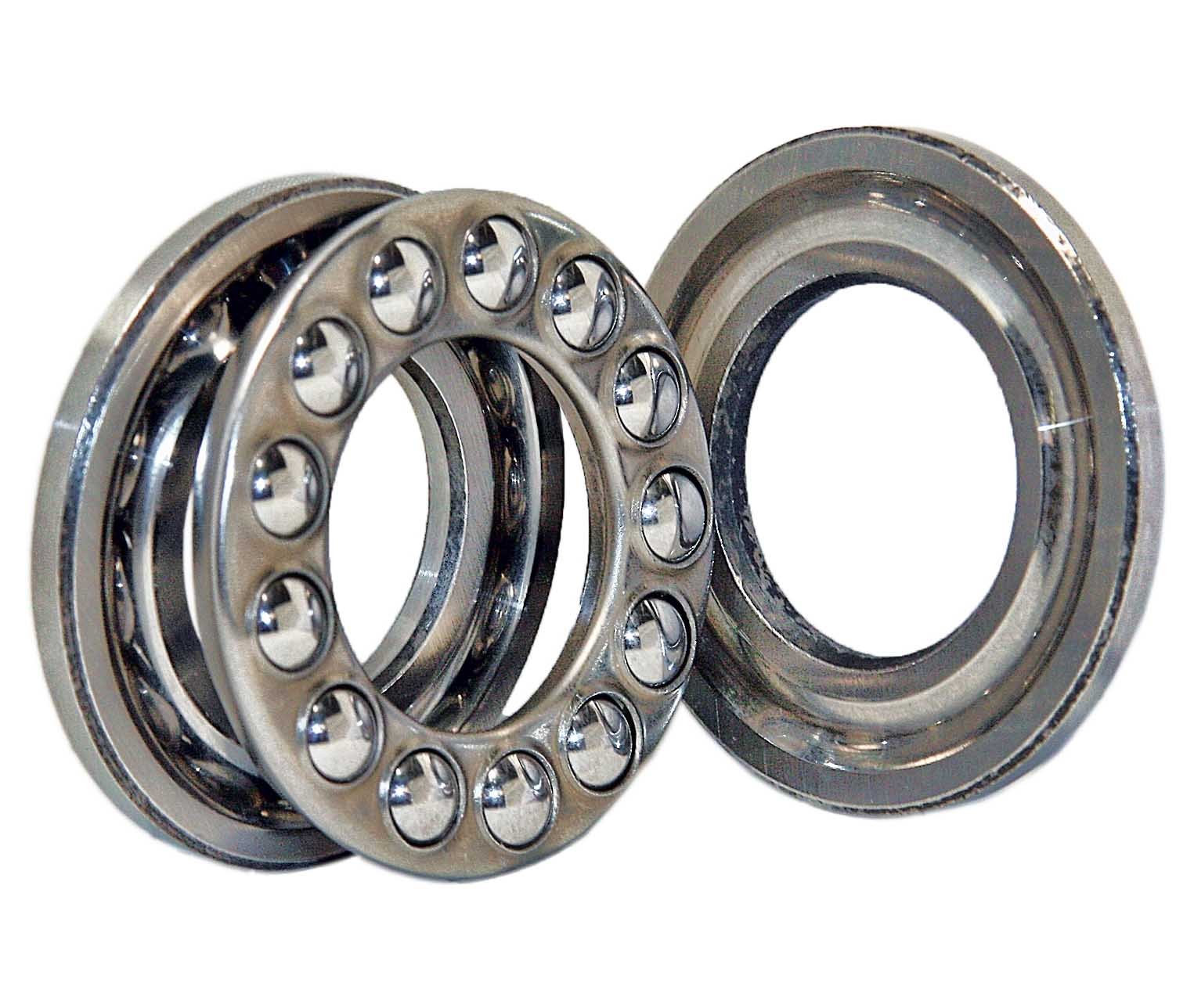

Ball Thrust Bearings
Thrust bearings are designed to support axial loads, which are forces parallel to the shaft's axis. They facilitate rotational movement between components while transferring axial forces from one part to another.
- Load Capacity: Typically supports axial loads up to 100 kN in low-speed applications.
- Operating Speed: Suitable for lower-speed applications, with maximum speeds of up to 3,000 RPM.
- Contact Angle: Common contact angles range from 30° to 90° for efficient axial load handling.
- Axial Load Capacity: Handles axial loads along the bearing axis, supporting high forces.
- High-Speed Capability: Offers low friction and supports high-speed rotation efficiently.
- Compact Design: Space-saving design fits into tight spaces in various applications.
- Directional Capability: Accommodates axial loads in one or both directions as needed.
- Precision: Ensures accurate alignment for smooth operation in demanding applications.
Types
- Ball Thrust Bearings: These bearings use balls as the rolling elements between the shaft washer and housing washer. They are suitable for applications requiring moderate axial load capacity and high-speed operation, such as automotive transmissions and machine tool spindles.
- Roller Thrust Bearings: Roller thrust bearings utilize cylindrical or tapered rollers to support higher axial loads compared to ball thrust bearings. They are used in heavy-duty applications, including industrial gearboxes, crane hooks, and large-scale machinery.
Features and Benefits

- Axial Load Capacity: Thrust bearings are optimized to handle axial loads efficiently, transferring forces along the bearing axis without significant radial load support.
- High-Speed Capability: Ball thrust bearings, in particular, offer low friction and high-speed operation, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid rotational speeds.
- Compact Design: Thrust bearings have a compact and space-saving design, making them ideal for applications where axial space is limited, such as automotive and aerospace applications.
- Directional Capability: They are designed to accommodate axial loads in one direction (unidirectional thrust bearings) or both directions (bidirectional thrust bearings), depending on the application requirements.
Applications

- Automotive: Thrust bearings are used in automotive applications such as transmissions, differential gears, and clutch assemblies to support axial loads and facilitate smooth operation under varying driving conditions.
- Aerospace: They play a critical role in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and flight control surfaces, providing reliable axial load support and precise movement.
- Industrial Machinery: Thrust bearings are essential in industrial equipment such as pumps, compressors, and machine tools, where they ensure efficient power transmission and support under axial loads.
Selection Considerations
- Load Ratings: Evaluate the magnitude of axial loads expected in the application and select thrust bearings with adequate load ratings to ensure reliable performance and longevity.
- Speed Capability: Consider the operating speed range and select bearings that can maintain stable operation at the desired speeds without excessive heat generation or wear.
- Lubrication Requirements: Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and methods to optimize bearing performance and prevent premature wear or damage.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess factors such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to contaminants to choose bearings with appropriate sealing or protective features for enhanced durability and reliability.
